China Economic Update 2021 Q1
China’s Gross domestic product (GDP) grew by 18.3% in the first quarter of 2021 compared with the first quarter of 2020, propelled by stronger demand at home and abroad and continued government support for SMEs. This marks the highest annual growth rate since China first began publishing GDP data in 1993, however, the high reading was skewed by the plunge in activity a year earlier when the economy shrank by 6.8%. The economy is still heavily reliant on public investment, and private consumption has not recovered as fast as hoped. The foundation for domestic economic recovery is not yet solid, with some service industries and SMEs still facing difficulties in production and operations. Increased prices for commodities and disruptions in international shipping logistics remain complicating factors for many companies.
As per the Q1 data, China’s Industrial Value Added (IVA) output went up 24.5 percent year on year in 2021 Q1 as factory activities continued to pick up. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) between 2019 and 2021 was 6.8%, in line with pre-pandemic IVA output growth. China’s fixed-asset investment (FAI) went up 25.6 percent year on year in 2021 Q1, with a CAGR of 2.9% in 2019-21, driven primarily by property investment in spite of tightening financing conditions for developers in place since January.
The Caixin China General Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI index), an important indicator of the strength of the Chinese economy, reached 50.6 in March, with a reading above 50 indicating an expansion in activity. The figure indicated that China’s manufacturing sector signalled a further improvement in operating conditions in March. Both supply and demand in the manufacturing sector has continued to expand, but the pace of that expansion has slowed for four straight months, which means the post-epidemic recovery was continuing to falter. The slower growth in both supply and demand added pressure to the labor market. The sector remained under employment pressure. In addition, although supply chain disruption eased, firms reported a sharp and accelerated rise in input costs during March amid reports of increased raw material prices. Notably, the rate of cost inflation was the steepest recorded for 40 months. The growing inflationary pressure limits the room for future policies and is not a good thing for sustaining an economic recovery in the postepidemic period.
In terms of the currency exchange rates, CAD/CNY fluctuated in Q1 2021, while overall an upward trend. Specifically, the exchange rate showed a strong momentum after the low 5.02 RMB on February 1 and reached to 5.24 RMB high on March 19.
2021 Economic Outlook
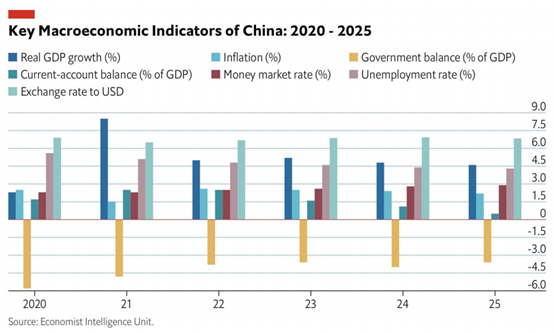
The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) under the Economist Group maintains its expectations that China’s real GDP will expand by 8.5% in 2021, up from 2.3% growth in 2020. This forecast sees growth as being underpinned by fiscal support for infrastructure, healthcare and consumption. Weak global demand and strained foreign relations will intensify calls for economic self-sufficiency via a new “dual circulation” model, which will also emphasize the importance of the domestic market.
The EIU predicts that following a strong year in 2021, GDP growth will stabilize around 5% over the following years, continuing an earlier pattern of gradual decline in growth. The unemployment rate is expected to maintain a position around 4.5%, after reaching close to 6% in 2020.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has forecasted an expansion of 8.4% for China’s GDP this year, up from an earlier forecast of 8.1%. The economy is likely to expand at the fastest pace in at least four decades as vaccine rollouts accelerate and advanced economies spend aggressively to counter the COVID-19 pandemic and related lockdowns.
The Construction Sector
According to the National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBS), the average new home prices in China’s 70 major cities rose by 4.6 percent year-on-year in March 2021, accelerating for a third straight month to the biggest annual gain since September, as strong property demand was enough to offset government cooling measures.
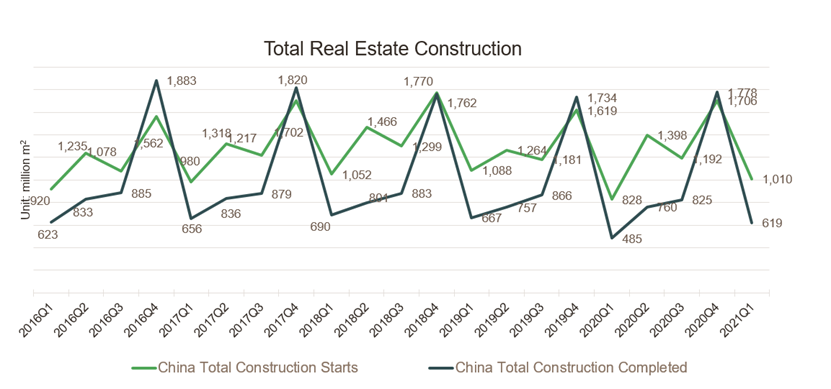
Total investment in real estate in China had a year-on-year increase of 25.6 percent from January to March. Total floor area completed in China in Q1 2021 was at 619.44 million m2.